Copenhagen Water Insights
Overall Score
Explore Copenhagen water insights and see how it exemplifies sustainable urban water management, balancing green infrastructure with advanced water technologies.
Copenhagen Water Insights
Overall Score
Explore Copenhagen water insights and see how it exemplifies sustainable urban water management, balancing green infrastructure with advanced water technologies.
Copenhagen Water Insights
✅ Overall Score
🏙️ Urban Planning Score
🌊 Flood Zones Management
📏 Water Levels
🏞️ Lakes and Reservoirs
🏖️ Beaches Score
🔧 Water Technologies
🏭 Desalination Plants
🌧️ Rain Capture Systems
🏞️ Rivers Score
🌊 Dams Score
🚰 Drainage Score
🌿 Sustainability Score
🌡️ Climate Vulnerability Score
💦 Water Quality Score
🌊 Water Flow Score
⚖️ Water Rights Score
🎣 Fishing Score
🚣 Recreation Score
☁️ Weather Patterns Score
🐟 Aquatic Life Score
🚢 Shipping and Ports Score
🏗️ Infrastructure Score
🌱 Native Flora Score
🦆 Wetlands Score
🏡 Residential Water Use
🏢 Commercial Water Use
🏥 Public Health Score
🗺️ Geographic Features Score
🛑 Water Restrictions Score
📊 Water Usage Statistics
🌐 Global Impact Score
📚 Educational Programs Score
🤝 Community Engagement
🏆 Awards and Recognition
📜 Historical Sites Score
🚨 Emergency Preparedness
🌈 Water Conservation Score
🛒 Water Market Score
Description
Copenhagen, Denmark, exemplifies sustainable urban water management, balancing green infrastructure with advanced water technologies.
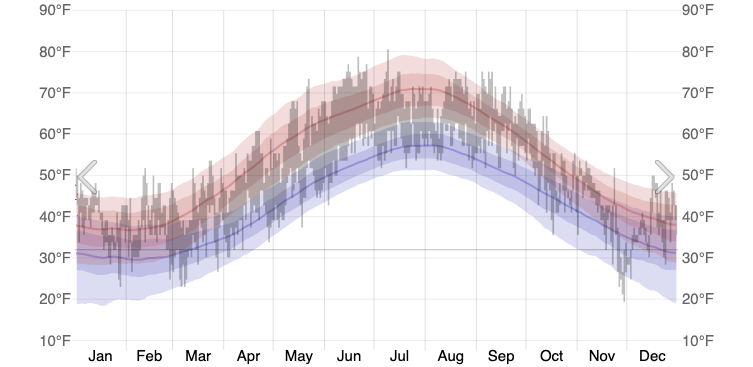
⛅️ Weather Now
🌍 Continent
Europe
🚩 Country
Denmark
👥 Population
Approximately 800,000 (2023)
💧 Water Management System
Managed by HOFOR, Greater Copenhagen Utility (HOFOR)
🌊 Flood Zones
Managed through green infrastructure and stormwater plans
📏 Water Levels
Monitored by HOFOR and local authorities
✈️ Living & Working Remotely
🏞️ Lakes and Reservoirs
Includes Lakes Sortedam, Peblinge, and Damhus
🏖️ Beaches
Amager Beach Park and Bellevue Beach. Checkout CoolContrast
🔧 Water Technologies
Advanced purification, stormwater management systems
🏭 Desalination Plants
None; relies on groundwater and treatment
🌧️ Rain Capture Systems
Extensive urban rain gardens and green roofs
🏞️ Rivers
Notable rivers include Harrestrup and Mølleåen
🌊 Dams
Few small dams, not a major water source
🚰 Drainage Systems
Combined sewer systems and modern drainage networks
🌿 Sustainability Initiatives
Copenhagen Climate Plan 2025 aims for carbon neutrality
🌡️ Climate Vulnerability
High risk from sea-level rise and heavy rainfall
💦 Water Quality Index
High, stringent EU-standard monitoring. Go to Tap Water to learn more.
🌊 Water Flow Rate
Controlled, with seasonal variation
⚖️ Water Rights and Regulations
Governed by Danish Ministry of Environment
🎣 Fishing Conditions
Allowed in designated areas, strict regulations
🚣 Recreational Water Activities
Popular for kayaking, sailing, and swimming
☁️ Weather Patterns
Temperate, with mild winters and cool summers
🐠 Aquatic Life
Freshwater fish, coastal marine species
🚢 Shipping and Ports
Port of Copenhagen, a major Nordic hub
🏗️ Water Infrastructure
Comprehensive, with flood protection systems
🌱 Native Flora
Oak, beech, and other temperate species
🦆 Wetlands
Includes Amager Nature Park, rich in biodiversity
🏡 Residential Water Usage
Around 104 liters per person per day
🏢 Commercial Water Usage
Regulated and monitored by HOFOR
🏥 Public Health and Water
High quality standards, frequent testing
🗺️ Geographic Features
Coastal city, islands, and peninsulas
🛑 Water Restrictions
Enforced occasionally during droughts
📊 Water Usage Statistics
Published by HOFOR and Ministry of Environment
🌐 Impact on Global Water
Model city for sustainable water management
📚 Water Education Programs
HOFOR’s school programs on sustainability
🤝 Community Engagement in Water Conservation
Strong public participation
🏆 Awards and Recognition for Water Stewardship
Known globally for green initiatives
📜 Historical Water Sites
Copenhagen Lakes, historical city water source
🚨 Emergency Water Preparedness
Detailed citywide contingency plans
🌈 Water Conservation Efforts
Active campaigns encouraging reduced use
🛒 Water Market and Economy
Utility fees fund sustainable projects
💼 Economic Impact of Water
Vital for tourism, ports, and green industries
Community Education and Water Conservation in Copenhagen
Copenhagen places significant emphasis on community education as a key part of its water management strategy. Through programs led by HOFOR, Greater Copenhagen Utility, the city educates residents of all ages about sustainable water practices and conservation, fostering a culture of shared responsibility.
School Programs and Hands-On Learning
Educational programs in schools introduce students to water conservation concepts from an early age. Interactive workshops and visits to water treatment facilities give students a real-world look at Copenhagen’s innovative water systems, encouraging them to appreciate and actively participate in sustainable water management.
Public Campaigns and Community Involvement
Public campaigns, including “Save Water” initiatives and the Copenhagen Climate Plan, engage residents in water-saving practices. These campaigns highlight practical steps for reducing water use at home and involve community members in activities such as rain garden installations and local green roof projects, strengthening public commitment to conservation.
The Role of HOFOR and Sustainability Workshops
HOFOR regularly hosts sustainability workshops and provides resources for citizens to learn more about Copenhagen’s green initiatives. These workshops cover topics like rainwater harvesting, reducing household water waste, and protecting local water quality, empowering residents to take proactive steps in conserving resources.
Cultivating a Water-Conscious Community
By integrating water conservation education into schools, public campaigns, and workshops, Copenhagen has cultivated a water-conscious community that actively contributes to the city’s environmental goals. This shared awareness ensures that sustainability remains a collective priority, reinforcing Copenhagen’s position as a global leader in water stewardship.
Urban Planning and Water Management in Copenhagen
Copenhagen’s urban planning is a model of sustainable, water-sensitive design, prioritizing resilience, green infrastructure, and efficient water management in every aspect of city development. By integrating flood prevention, rainwater capture, and eco-friendly landscapes into its urban layout, Copenhagen has created a city that is both livable and resilient to climate challenges.
Green Infrastructure for Water Management
Copenhagen’s commitment to green infrastructure is evident in its widespread use of rain gardens, green roofs, and permeable surfaces, which naturally filter and absorb rainwater. These features not only beautify the city but also help mitigate flooding and reduce pressure on the drainage system, making Copenhagen more resilient during periods of heavy rainfall.
Flood Prevention and Climate Adaptation
Copenhagen’s urban planning addresses the risks posed by sea-level rise and intense storms, using solutions like stormwater reservoirs, coastal defenses, and elevated urban spaces. Projects like the Copenhagen Climate Adaptation Plan aim to protect the city from flooding by diverting and storing excess water in times of high rainfall, ensuring that public and private spaces remain safe and functional.
Multi-Purpose Spaces for Water Storage and Recreation
Copenhagen combines functionality with recreation, transforming water management infrastructure into community spaces. For example, parks and recreational areas double as temporary water storage during storms, blending utility with public enjoyment. This multi-purpose approach enhances urban livability while ensuring water management remains efficient and unobtrusive.
Smart Planning and Efficient Water Use
Through strict zoning laws and water-efficient building regulations, Copenhagen ensures that all new developments align with sustainability goals. Water-saving devices, eco-friendly landscaping, and sustainable building materials are encouraged in both residential and commercial areas, reducing overall water consumption and contributing to long-term sustainability.
Conclusion
Copenhagen’s urban planning is an exemplary blend of sustainability and resilience. By integrating green infrastructure, flood management, and smart urban design, the city protects its water resources and enhances residents’ quality of life, setting a global benchmark for sustainable city planning.
Sustainability and Conservation in Copenhagen’s Water Management
Copenhagen leads the way in sustainable water management, embedding conservation practices into its infrastructure, policies, and community engagement. Through innovative water reuse, green technologies, and climate resilience initiatives, the city demonstrates how urban areas can effectively conserve resources while fostering environmental stewardship.
Water Reuse and Rainwater Harvesting
Copenhagen is committed to maximizing water reuse. Rainwater is captured through rain gardens, green roofs, and permeable pavements, reducing runoff and conserving potable water. This approach not only lessens demand on treated water supplies but also alleviates pressure on drainage systems, especially during heavy rainfall.
Green Infrastructure and Energy-Efficient Technologies
Copenhagen integrates green infrastructure into its urban landscape to support water conservation. Parks, green rooftops, and bioswales are strategically designed to absorb rainwater and reduce urban runoff, while energy-efficient water treatment facilities minimize the environmental impact of water processing and distribution.
Climate Adaptation and Flood Resilience
Copenhagen’s Climate Adaptation Plan addresses water conservation within the context of climate resilience. By investing in flood defenses, stormwater storage areas, and coastal barriers, the city protects itself from rising sea levels and extreme weather, reducing water waste and preventing damage to water-sensitive infrastructure.
Community Engagement in Conservation
Public campaigns and educational programs encourage Copenhagen’s residents to adopt sustainable practices, such as reducing water consumption at home and participating in rainwater harvesting projects. This strong culture of conservation and responsibility among citizens plays a crucial role in achieving the city’s sustainability goals.
Conclusion
Copenhagen’s approach to sustainability and water conservation demonstrates a holistic model that combines green infrastructure, technology, and community involvement. As the city continues to innovate, it remains a global leader in sustainable urban water management and a beacon of environmental stewardship.
Infrastructure and Technology in Copenhagen’s Water Management
Copenhagen’s water management infrastructure is a model of innovation, sustainability, and resilience. Integrating cutting-edge technology and eco-friendly infrastructure, the city optimizes water conservation, flood prevention, and climate adaptation. Managed by HOFOR, Copenhagen’s water systems demonstrate how urban areas can secure their water future through intelligent design and smart solutions.
Advanced Water Treatment and Distribution
Copenhagen’s water treatment facilities use state-of-the-art technologies to ensure clean, safe drinking water with minimal environmental impact. Energy-efficient filtration and purification systems allow HOFOR to meet high-quality standards while conserving resources. Smart distribution systems monitor and control water flow, preventing leaks and reducing waste.
Smart Flood Management Systems
As a coastal city vulnerable to flooding, Copenhagen invests heavily in smart flood management. Stormwater retention basins, green roofs, and permeable pavements help absorb and store rainwater, protecting urban areas from heavy rainfall. Technologies such as real-time water level monitoring and automated control systems allow for responsive flood mitigation, safeguarding public infrastructure.
Rainwater Harvesting and Green Infrastructure
Copenhagen uses green infrastructure, including rain gardens, bioswales, and rainwater harvesting systems, to collect and repurpose rainwater. These features not only reduce runoff but also help recharge groundwater levels and support sustainable urban landscaping. By incorporating these systems into urban planning, Copenhagen manages rainwater efficiently and promotes water reuse.
Digital Innovations for Monitoring and Efficiency
Digital solutions play a critical role in Copenhagen’s water management, with HOFOR utilizing data analytics, IoT sensors, and smart meters to track water consumption, quality, and flow in real-time. This data-driven approach helps optimize water usage, detect issues early, and improve overall system efficiency.
Conclusion
Copenhagen’s blend of innovative infrastructure and advanced technology makes it a global leader in sustainable water management. By leveraging smart flood systems, green infrastructure, and digital monitoring, Copenhagen ensures a resilient, efficient, and environmentally friendly water system that meets the needs of a modern city.
Water Management System in Copenhagen
Copenhagen’s water management system, led by HOFOR (Greater Copenhagen Utility), is a benchmark of sustainability and resilience, combining advanced infrastructure, smart technologies, and green initiatives. Designed to meet the city’s growing needs while mitigating climate risks, Copenhagen’s approach prioritizes water quality, flood prevention, and community engagement.
Sustainable Water Sourcing and Treatment
Copenhagen’s water management focuses on local groundwater as the primary source, ensuring a steady and sustainable supply. Advanced treatment facilities utilize energy-efficient filtration and purification methods to maintain high water quality standards with minimal environmental impact, ensuring safe drinking water for residents while conserving resources.
Flood Management and Climate Resilience
Given its coastal location, Copenhagen faces significant flood risks from rising sea levels and heavy rainfall. The city has implemented comprehensive flood management infrastructure, including stormwater retention basins, permeable pavements, and green roofs, which absorb rainwater and prevent urban flooding. These green solutions are bolstered by digital water level monitoring and automated controls, allowing for rapid response during extreme weather events.
Rainwater Harvesting and Reuse
Copenhagen incorporates rainwater harvesting into its water management system, capturing rainwater through green infrastructure like rain gardens and bioswales. This harvested water reduces the burden on potable water supplies and supports sustainable urban landscaping, creating a circular approach to water use in the city.
Public Education and Community Involvement
Copenhagen’s water management strategy includes robust community engagement. Public campaigns and educational programs inform residents about water conservation practices and involve them in projects like rainwater harvesting and green roof installations. This collective effort ensures that conservation becomes a shared value within the community.
Conclusion
Copenhagen’s water management system exemplifies a sustainable, future-ready model by blending advanced technology, green infrastructure, and community involvement. Through careful sourcing, efficient treatment, flood resilience, and public engagement, Copenhagen has built a water system that meets modern demands while safeguarding against climate risks.
Water Resource Availability in Copenhagen
Copenhagen’s approach to water resource availability emphasizes sustainability, local sourcing, and efficient use to ensure a resilient supply for its growing urban population. Groundwater forms the city’s primary water source, supported by rainwater harvesting and cutting-edge conservation strategies managed by HOFOR (Greater Copenhagen Utility).
Groundwater as the Primary Source
Copenhagen relies predominantly on locally-sourced groundwater, extracted and treated to meet high drinking water standards. This focus on groundwater not only ensures a consistent supply but also minimizes the environmental impact associated with long-distance water transport, reinforcing the city’s commitment to sustainable sourcing.
Rainwater Harvesting and Green Infrastructure
Rainwater harvesting is integral to Copenhagen’s water strategy, reducing reliance on groundwater and mitigating the effects of heavy rainfall. By using green infrastructure, such as rain gardens, bioswales, and permeable pavements, Copenhagen effectively captures and utilizes rainwater, supporting sustainable landscaping and relieving pressure on drainage systems.
Climate-Responsive Water Management
In the face of climate challenges, including sea-level rise and increased rainfall, Copenhagen adapts its water resource strategy to enhance resilience. Flood defenses, stormwater storage, and adaptable infrastructure allow the city to manage water effectively during extreme weather, ensuring availability and protecting against shortages.
Community Awareness and Conservation
Community engagement is a cornerstone of Copenhagen’s approach to water resource availability. Through public education campaigns and programs, residents are encouraged to practice water conservation, helping to reduce demand and sustain resources for the future.
Conclusion
Copenhagen’s water resource availability strategy balances local sourcing, rainwater capture, and community conservation. By focusing on sustainable practices and resilience to climate change, the city secures its water future and provides a model of eco-conscious resource management for other urban centers.
Environmental Impact of Water Management in Copenhagen
Copenhagen’s water management system is designed to minimize environmental impact while meeting the needs of a growing urban population. By prioritizing sustainable practices, efficient water use, and green infrastructure, the city reduces its ecological footprint and enhances environmental resilience.
Low-Impact Water Sourcing and Treatment
Copenhagen’s reliance on groundwater and minimal chemical use in water treatment reduces pollution and energy consumption. This approach not only safeguards the environment but also protects local ecosystems from potential contaminants, supporting a healthier natural environment.
Green Infrastructure for Stormwater Management
Copenhagen integrates green infrastructure—like rain gardens, green roofs, and permeable pavements—into its urban landscape to manage stormwater naturally. These features absorb and filter rainwater, preventing urban runoff from polluting local waterways and reducing the load on the city’s drainage system. This method protects aquatic habitats and prevents erosion, preserving biodiversity.
Climate Adaptation for Resilience
Facing climate-related threats such as rising sea levels and increased rainfall, Copenhagen employs adaptive water management solutions. Flood defenses, coastal barriers, and stormwater retention systems protect both urban and natural areas from damage, ensuring that the city’s water management system remains resilient to environmental changes.
Community Role in Conservation and Awareness
Copenhagen encourages residents to adopt sustainable practices through public campaigns and education, fostering a community-wide commitment to environmental stewardship. By involving the public in conservation efforts, Copenhagen builds a city culture that supports long-term environmental health.
Conclusion
Copenhagen’s water management system prioritizes environmental impact reduction through sustainable sourcing, green infrastructure, and climate resilience. As a result, Copenhagen sets a high standard for environmentally responsible urban water management, balancing the needs of its residents with the preservation of natural resources and ecosystems.
More on Copenhagen Water Insights & Management
Get notified on new water management news, updates & advancements in Copenhagen.
Shop Books, eBooks, Audiobooks

The Little Book on Hydration: The People’s Guide To Health, Vitality & Flow (Audiobook)

Water Wise: Sustainable Living in a Modern World

Thirsty Planet: A Journey Through Water Scarcity and Solutions

Atmospheric Water Generators: And How to Build One

Collecting the Skies: A Guide to Rainwater Harvesting

The Little Book on Hydration: The People’s Guide To Health, Vitality & Flow
Copenhagen Weather Right Now
Reviews of Copenhagen Water Management
There are no reviews yet. Be the first one to write one.
There are no reviews yet. Be the first one to write one.